Move To iOS marks a significant shift for many smartphone users, presenting a compelling alternative to the Android ecosystem. This guide delves into the key aspects of transitioning from Android to iOS, providing a detailed comparison of user experiences, app ecosystems, hardware options, and cost considerations. We’ll explore the advantages and disadvantages of each platform, helping you make an informed decision about switching.
From comparing the onboarding processes and UI designs to navigating the complexities of data transfer and app equivalence, we’ll provide a step-by-step walkthrough of the transition. We’ll also analyze the long-term value proposition of investing in the Apple ecosystem, including security and privacy considerations. This in-depth analysis will equip you with the knowledge needed to confidently navigate the switch to iOS.
Switching from Android to iOS: A User’s Perspective: Move To Ios
Migrating from the Android ecosystem to iOS presents a significant shift in user experience. This transition involves adapting to a new operating system, interface, and app ecosystem. This section details the key differences, data transfer process, and app comparisons to aid in a smoother transition.
The move to iOS often involves integrating smart home devices, and users are frequently searching for compatibility solutions. One popular method involves using Homebridge, and for those with Feit Electric bulbs, setting up the connection requires understanding the specifics detailed in this helpful guide: feit homebridge. Successfully configuring this expands the smart home capabilities available within the iOS ecosystem.
Android and iOS Onboarding: A Comparison
Both Android and iOS offer streamlined onboarding processes for new users. Android typically focuses on a quick setup using a Google account, emphasizing integration with Google services. iOS prioritizes Apple ID integration, focusing on iCloud services and Apple’s ecosystem. Both platforms offer intuitive guides, but the initial setup reflects the core philosophy of each operating system: Android’s open approach versus iOS’s integrated ecosystem.
User Interface Design Philosophies
Source: hindustantimes.com
Android’s UI design is known for its flexibility and customization options, offering widgets and extensive settings for personalization. iOS emphasizes simplicity and ease of use, prioritizing a clean, minimalist aesthetic and intuitive navigation. This difference reflects a fundamental contrast in design philosophies: Android’s emphasis on user control versus iOS’s focus on streamlined user experience.
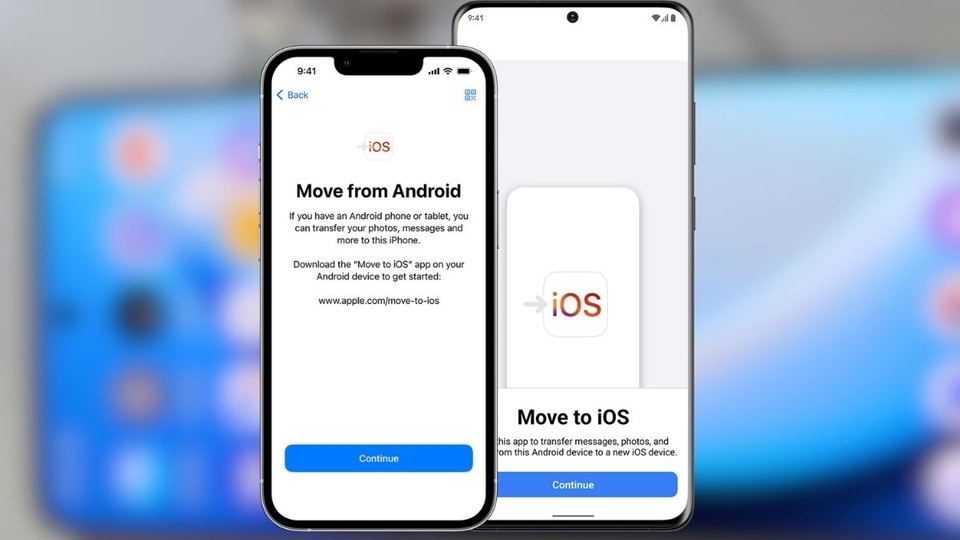
Transferring Data from Android to iOS
Transferring data from Android to iOS can be achieved using Apple’s “Move to iOS” app. This app facilitates the transfer of contacts, messages, photos, videos, and calendar events. The process involves installing the app on the Android device, connecting both devices to the same Wi-Fi network, and following the on-screen prompts. Ensure both devices are sufficiently charged before initiating the transfer.
- Download and install “Move to iOS” on your Android device.
- On your new iOS device, start the setup process until you reach the “Apps & Data” screen.
- Select “Move Data from Android.”
- On your Android device, open the “Move to iOS” app and follow the on-screen instructions to generate a unique code.
- Enter the code on your iOS device.
- Select the data you want to transfer.
- Wait for the transfer to complete. This may take some time depending on the amount of data.
Common Android and iOS Apps: A Comparison
Many popular apps are available on both platforms, but functionalities can vary. The following table compares some key apps.
| App Name (Android) | App Name (iOS) | Key Features | Differences in Functionality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Maps | Apple Maps | Navigation, street view, location sharing | Differences in map data, voice navigation features, and integration with other Apple services. |
| Gmail | Gmail | Email management, calendar integration | Generally consistent functionality across platforms, though minor UI differences exist. |
| Google Photos | Photos | Photo storage, sharing, editing | Different cloud storage integration (Google Photos vs. iCloud), minor differences in editing tools. |
| Messaging, voice and video calls | Generally consistent across platforms. |
iOS Ecosystem and App Store: Strengths and Weaknesses
Apple’s app ecosystem, centered around the App Store, differs significantly from Google Play. This section analyzes the strengths and weaknesses of this ecosystem, considering app curation, exclusive apps, and pricing.
App Store Curation and App Quality
The App Store’s rigorous curation process aims to maintain a high standard of app quality. This process involves reviewing apps for functionality, security, and adherence to Apple’s guidelines. While this leads to a generally higher quality app experience, it can also result in a slower app approval process and stricter limitations on app functionality compared to Google Play’s more open approach.
Exclusive iOS Apps and Features
Apple’s ecosystem boasts several exclusive apps and features unavailable on Android. Examples include iMessage for seamless communication within the Apple ecosystem, FaceTime for video calls, and apps leveraging Apple’s hardware features like the LiDAR scanner in some iPhone models for augmented reality applications. These exclusive apps enhance the user experience within Apple’s walled garden.
iOS vs. Android App Pricing: A Comparison
App pricing can vary between iOS and Android. While many apps are priced similarly, some may have different pricing strategies or offer different in-app purchase options. The table below provides examples.
| App Name | iOS Price | Android Price | Price Difference Justification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adobe Lightroom Mobile | Subscription model | Subscription model | Generally consistent pricing across platforms |
| Procreate | One-time purchase | N/A | App exclusively available on iOS |
| Microsoft Office Suite | Subscription or one-time purchase (varies by app) | Subscription or one-time purchase (varies by app) | Pricing may vary slightly based on platform-specific features. |
Choosing an iOS Device: Hardware Considerations
Selecting an iPhone model requires careful consideration of various factors, including screen size, storage capacity, processing power, and budget. This section categorizes iPhone models to assist in making an informed decision.
iPhone Model Comparison: Features and Target Audience
Apple offers a range of iPhones catering to different needs and budgets. Models are typically categorized by price and features. Generally, higher-priced models offer enhanced features such as improved cameras, faster processors, larger displays, and increased storage capacity.
iPhone Model Categories: Pros and Cons
- Budget-Friendly iPhones: Pros: Affordable price point, essential features. Cons: Smaller storage options, less powerful processors, older designs.
- Mid-Range iPhones: Pros: Balance of price and features, improved camera systems, larger displays. Cons: May lack the most advanced features of flagship models.
- Flagship iPhones: Pros: Cutting-edge features, powerful processors, best camera systems, larger displays, more storage options. Cons: Highest price point.
Cost and Value: Analyzing the iOS Investment
The total cost of ownership for an iOS device compared to an Android device should be considered over the long term. This includes initial device cost, app purchases, potential repair costs, and resale value.
Total Cost of Ownership: iOS vs. Android, Move To Ios
A three-year comparison might show a higher initial cost for an iPhone, but this can be offset by factors like longer software support, potential higher resale value, and potentially lower repair costs due to better build quality (depending on the specific models compared). However, this is a generalized comparison and actual costs can vary significantly based on usage and specific models chosen.
Long-Term Value and Resale Value
iPhones generally hold their resale value better than many Android phones, potentially mitigating the higher initial cost over the long term. Apple’s reputation for software updates and long-term support contributes to this higher resale value. This needs to be considered against the cost of potential repairs, app purchases, and subscription services.
iOS Device Pricing Tiers and Features
Apple’s pricing tiers reflect the range of features offered. Generally, higher-priced models offer superior cameras, more processing power, increased storage, and larger displays. This pricing strategy allows consumers to choose a device that best suits their needs and budget.
Security and Privacy on iOS: A Comparative Analysis
Both iOS and Android offer security and privacy features, but their approaches differ significantly. This section compares these approaches and highlights key differences.
iOS and Android Security and Privacy Features
iOS emphasizes a more centralized and controlled approach to security and privacy, with features like strong encryption, app sandboxing, and privacy-focused settings. Android offers a more open and customizable approach, with various security features available but requiring more user intervention and configuration. Both platforms are constantly evolving their security measures.
Apple’s Approach to User Data Privacy
Apple has positioned itself as a strong advocate for user data privacy. Their approach involves limiting data collection, providing users with transparent controls over their data, and actively opposing government requests for user data unless legally mandated.
Security Risks: iOS vs. Android
Both operating systems face potential security risks, such as malware and phishing attacks. The open nature of Android can potentially make it more susceptible to certain types of attacks, while iOS’s more controlled environment may offer some inherent protection. Regular software updates and cautious online behavior are crucial for minimizing risks on both platforms.
Security Feature Comparison: iOS vs. Android
A simplified comparison shows iOS prioritizing built-in security features and user privacy controls, while Android offers a more customizable security landscape requiring more user involvement. Both systems have strengths and weaknesses, with the best choice depending on individual needs and technical expertise.
Last Point
Ultimately, the decision to move to iOS is a personal one, dependent on individual needs and priorities. However, by carefully weighing the factors discussed—user experience, app ecosystem, hardware choices, cost, and security—potential switchers can make a well-informed choice. This comprehensive guide has aimed to provide the necessary information to facilitate a smooth and successful transition, empowering users to embrace the iOS experience with confidence.