Target recruitment process is crucial for organizations seeking specialized talent. This strategic approach, unlike general recruitment, focuses on attracting candidates with specific skills and experience to fill critical roles. It involves a meticulous process of identifying, attracting, assessing, and onboarding individuals who precisely match the company’s needs. This detailed guide will explore each step, highlighting best practices and addressing common challenges.
From defining target profiles and employing effective sourcing strategies to crafting compelling employer branding and navigating legal considerations, we will unpack the intricacies of a successful target recruitment process. We’ll delve into various assessment methods, onboarding strategies, and techniques for measuring and improving the overall effectiveness of the program. Real-world case studies will illustrate the practical application of these principles across diverse industries.
Target Recruitment: A Strategic Approach to Hiring: Target Recruitment Process
In today’s competitive landscape, attracting top talent is crucial for business success. General recruitment methods often fall short when seeking specialized skills or filling highly demanding roles. Target recruitment, a more strategic and focused approach, offers a solution. This process involves identifying, attracting, and onboarding candidates with specific skills and experience to meet precise organizational needs.
Defining Target Recruitment
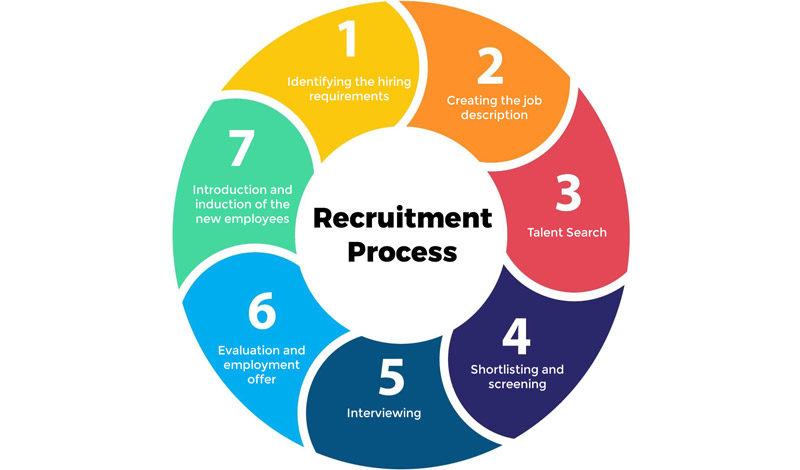
Source: 2coms.com
Target recruitment is a proactive and highly selective approach to hiring that focuses on attracting specific individuals with pre-defined skills and experience. It contrasts with general recruitment, which casts a wider net. A successful target recruitment strategy is characterized by a clear understanding of the target audience, a well-defined selection process, and the use of effective channels to reach potential candidates.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) used to measure effectiveness include time-to-hire, cost-per-hire, quality of hire, and candidate satisfaction.
Identifying Target Candidates
Identifying ideal candidates within niche industries requires a multi-pronged approach. Effective sourcing strategies for hard-to-fill roles include leveraging professional networking platforms like LinkedIn, attending industry conferences, engaging with niche job boards, and conducting direct outreach to passive candidates. A robust candidate evaluation process involves creating a detailed scoring rubric that aligns with the job description’s requirements, enabling objective comparisons between candidates.
Attracting Target Candidates
Creating a compelling employer brand message that resonates with target candidates is crucial. This involves highlighting unique company culture, values, and employee benefits. Effective job descriptions should clearly articulate the role’s responsibilities, required skills, and career progression opportunities. Multiple recruitment channels are necessary to reach specific target audiences. A diverse approach maximizes reach and increases the chances of attracting high-quality candidates.
| Channel | Pros | Cons | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large professional network, targeted advertising options | Can be expensive, requires skilled management | High (depending on advertising spend) | |
| Niche Job Boards | Targeted reach to specific industries | Smaller audience than general job boards | Medium (varies depending on board and posting fees) |
| Employee Referrals | High-quality candidates, lower cost | Limited reach, potential for bias | Low (often involves bonuses or incentives) |
| Direct Outreach | Personalized approach, high engagement potential | Time-consuming, requires strong research skills | Low (primarily time investment) |
Assessing Target Candidates
Effective screening processes, such as resume screening and initial phone interviews, filter out unsuitable candidates. Structured interviews, designed to assess specific skill sets through standardized questions and scoring rubrics, provide a fair and objective evaluation. Various assessment methods, including skills tests, personality assessments, and case studies, can be used to evaluate candidate suitability, providing a holistic view of their capabilities.
Onboarding Target Candidates
A comprehensive onboarding program tailored to the needs of target hires is vital for their early success. This includes a structured orientation, clear role expectations, and opportunities for mentorship. A checklist of essential steps, such as setting up accounts, assigning mentors, and providing necessary training, ensures a smooth transition. Regular check-ins and feedback sessions help new hires integrate into the company culture and address any challenges they may face.
Measuring and Improving Target Recruitment
Tracking key metrics, such as time-to-fill, cost-per-hire, and quality of hire, allows for continuous monitoring of the recruitment process’s effectiveness. Analyzing recruitment data can identify bottlenecks, areas for improvement, and potential biases. Regular process reviews and adjustments based on data analysis optimize the target recruitment process and ensure its continued success.
Legal and Ethical Considerations, Target recruitment process
Target recruitment practices must comply with all applicable laws and regulations to avoid legal pitfalls. Ethical considerations require careful attention to avoid discrimination against specific demographic groups. Best practices include using objective criteria in candidate selection, ensuring fair and inclusive recruitment processes, and providing equal opportunities to all qualified applicants.
Case Studies of Successful Target Recruitment
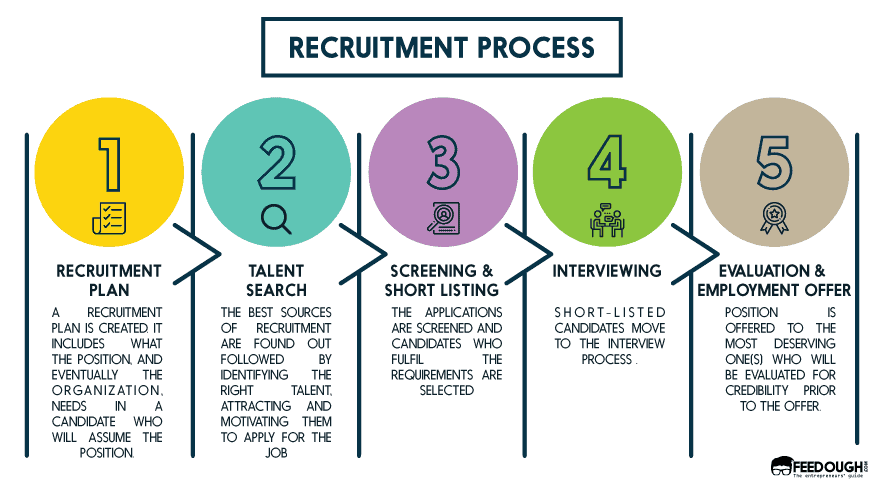
Source: feedough.com
Several companies have successfully implemented target recruitment strategies. For example, a tech startup targeting experienced data scientists used a combination of LinkedIn recruitment, attending industry conferences, and direct outreach to passive candidates, resulting in a 50% reduction in time-to-hire and a significant improvement in the quality of hires. Another example is a financial institution that used employee referrals and internal mobility programs to fill specialized roles, achieving cost savings and improved employee retention.
- Case Study 1: Tech Startup Data Scientist Recruitment
- Target Audience: Experienced data scientists with specific programming languages and machine learning experience.
- Methods Used: LinkedIn, industry conferences, direct outreach.
- Results: 50% reduction in time-to-hire, improved quality of hire.
- Case Study 2: Financial Institution Specialized Roles
- Target Audience: Experienced financial analysts and risk managers.
- Methods Used: Employee referrals, internal mobility programs.
- Results: Cost savings, improved employee retention.
Last Point
Mastering the target recruitment process is essential for organizational success in today’s competitive talent landscape. By carefully defining target profiles, employing strategic sourcing, and implementing robust assessment and onboarding strategies, companies can attract and retain top-tier talent. Continuous monitoring and improvement of the process, alongside adherence to ethical and legal guidelines, are key to building a high-performing workforce.
The strategies Artikeld in this guide provide a roadmap for organizations to effectively navigate the complexities of targeted recruitment and achieve their talent acquisition goals.